 |
Homo & hetero-oligomeric foldomes of functional and pathological amyloids |
||
|
Challenge: Neurodegeneration CSIC White books:
PI: Miguel Mompeán |
|||
|
Critical aspects relating protein aggregation to cell function and human disease are still unknown. We wish to understand what structural, thermodynamic and kinetic factors drive the preferential assembly of some aggregate forms over others (e.g. homo- versus hetero-amyloids versus intrinsically disordered forms within condensates). Using and re-thinking advanced NMR methods in solution and in the solid-state, including hyperpolarization schemes and a myriad of computational approaches, we aim to identify the defining features of functional versus pathological aggregate forms in relevant health-related proteins, including TDP-43, nucleoporins and RIP kinases and other RHIM-containing proteins. This knowledge is ultimately used to design new proteins that modulate distinct aggregation events
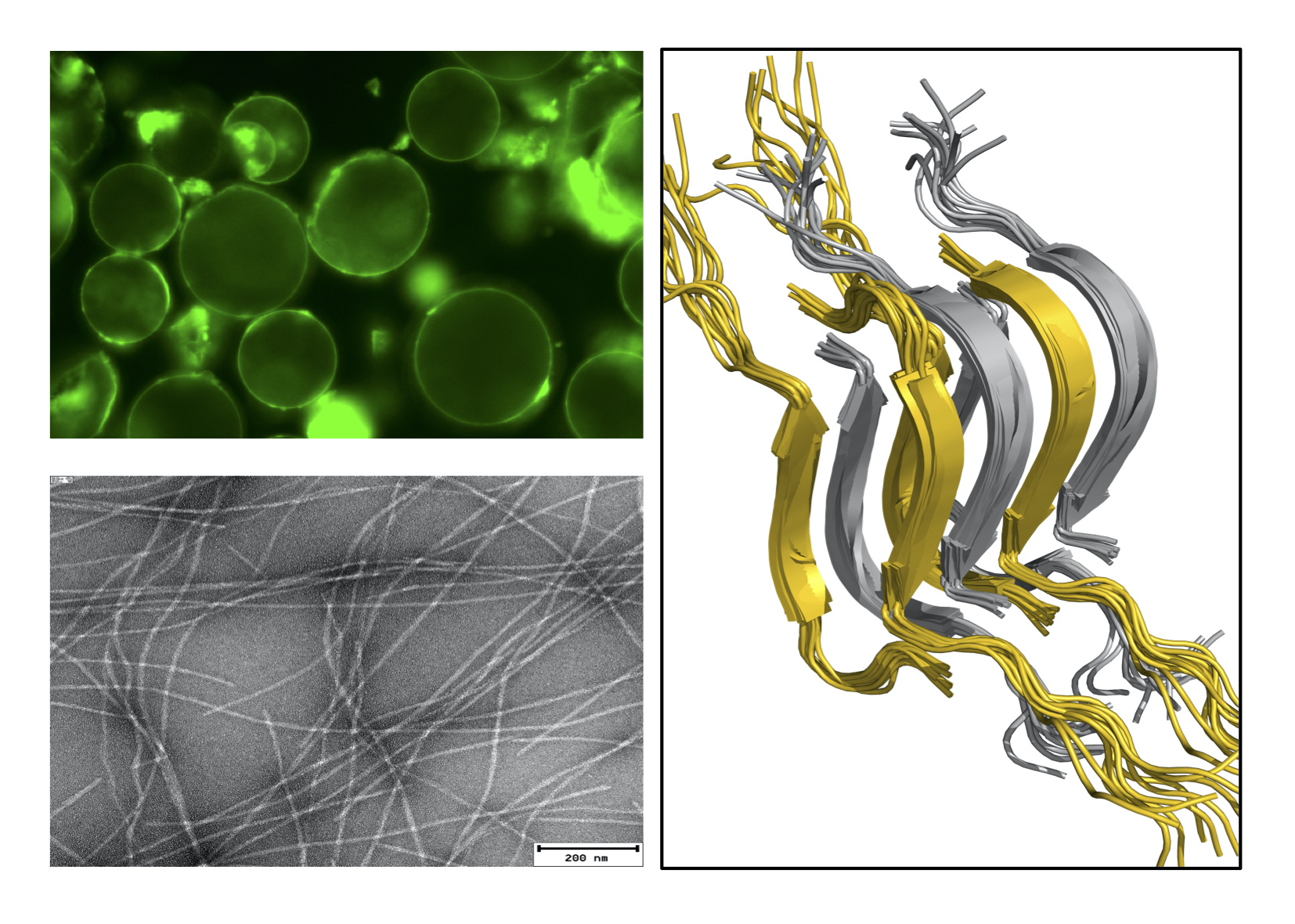
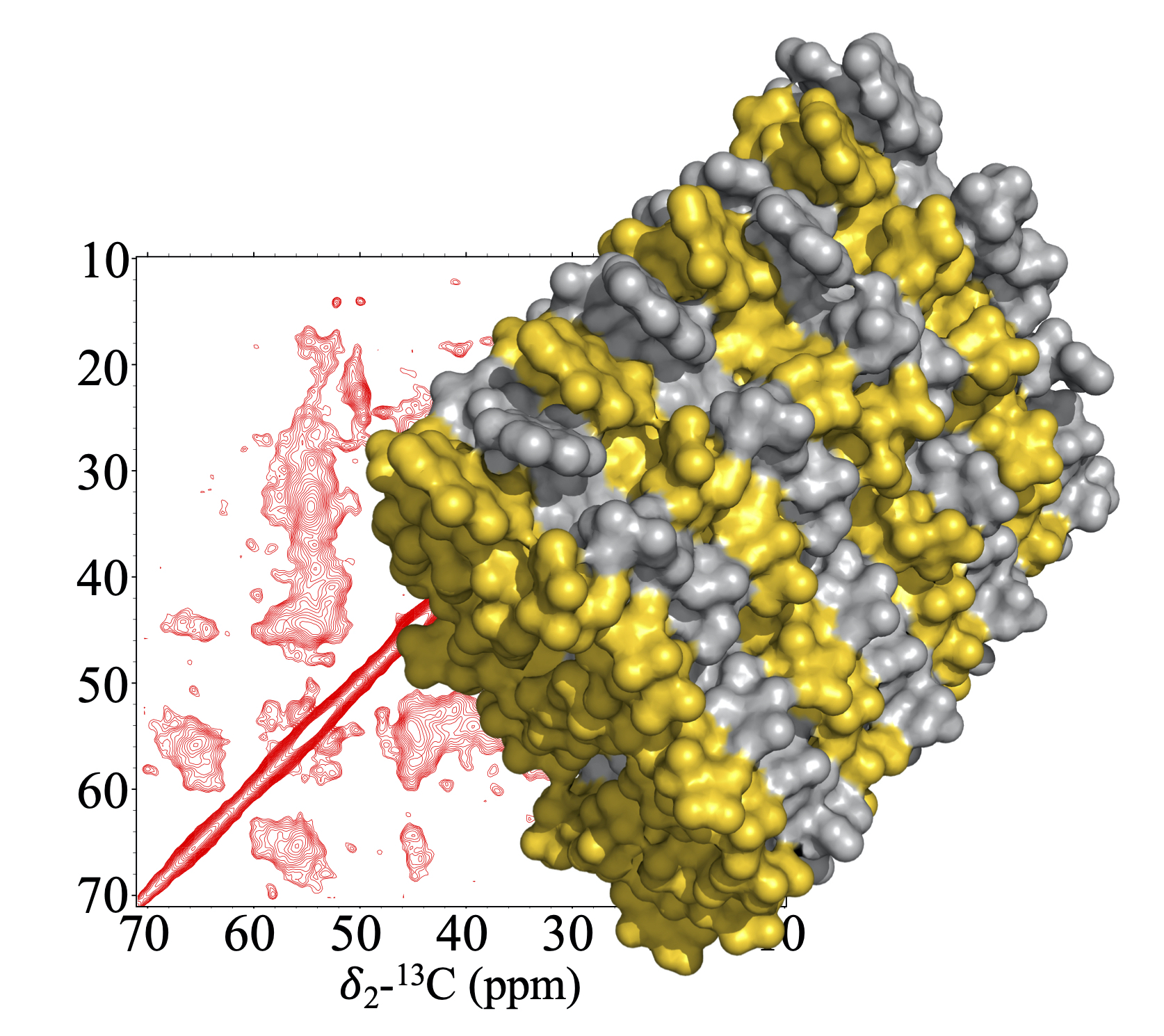
In the figure, a droplet (top left) and a fibril form (bottom left) of a protein, and the structural model of a hetero-amyloid (right).
Publications Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2021 In Press
SUMOylation Regulates TDP-43 Splicing Activity and Nucleocytoplasmic Distribution.
Mol Neurobiol. 2021 Aug 14. doi: 10.1007/s12035-021-02505-8. Online ahead of print. PMID: 34390468
Phe-Gly motifs drive fibrillization of TDP-43's prion-like domain condensates.
PLoS Biol. 2021 Apr 28;19(4):e3001198. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3001198. eCollection 2021 Apr. PMID: 33909608
NMR assignments for the C-terminal domain of human TDP-43.
Biomol NMR Assign. 2021 Apr;15(1):177-181. doi: 10.1007/s12104-020-10002-7. Epub 2021 Jan 8. PMID: 33417141
Molecular mechanism of the inhibition of TDP-43 amyloidogenesis by QBP1.
Arch Biochem Biophys. 2019 Oct 30;675:108113. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2019.108113. Epub 2019 Sep 27. PMID: 31568752
Mimicry by a viral RHIM.
EMBO Rep. 2019 Feb;20(2):e47433. doi: 10.15252/embr.201847433. Epub 2019 Jan 21. PMID: 30665943
Dysregulation of TDP-43 intracellular localization and early onset ALS are associated with a TARDBP S375G variant.
Brain Pathol. 2019 May;29(3):397-413. doi: 10.1111/bpa.12680. Epub 2018 Dec 27. PMID: 30461104
Full list:
Collaborators
Financing
|
|||